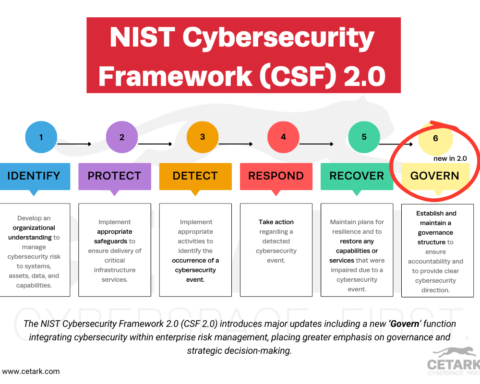
What exactly is phishing, and how can you recognize and prevent it? Our Phishing 101 guide cuts through the complexity to deliver straightforward insights into identifying phishing attempts and safeguarding your information against these deceptive practices.
Key Takeaways
- Phishing is a cybercrime strategy to deceive individuals into providing sensitive information via emails, websites, and social media, sometimes imitating known entities through social engineering.
- Phishing methods are diverse and evolve with technology, ranging from generalized email phishing to more targeted techniques like spear phishing, vishing (voice), and smishing (SMS), each designed to exploit specific vulnerabilities.
- Protection against phishing involves vigilance in recognizing scam characteristics, using security tools, exercising caution with personal information, educating oneself and others about emerging threats and reporting suspicious activities.
Understanding Phishing: Definition and Purpose
 Phishing is a method employed by cybercriminals to illicitly obtain sensitive information, like bank account numbers, through deceitful requests via email or websites. Imagine a digital wolf in sheep’s clothing, cunningly disguised to trick the unsuspecting victim into revealing their secrets. The main objective of phishing attacks is to unlawfully obtain data, financial resources, or both, often by directing victims to a malicious link or website where they are tricked into providing sensitive information.
Phishing is a method employed by cybercriminals to illicitly obtain sensitive information, like bank account numbers, through deceitful requests via email or websites. Imagine a digital wolf in sheep’s clothing, cunningly disguised to trick the unsuspecting victim into revealing their secrets. The main objective of phishing attacks is to unlawfully obtain data, financial resources, or both, often by directing victims to a malicious link or website where they are tricked into providing sensitive information.
Phishing attacks employ various methods to impersonate trusted entities, such as pretending to be someone else or other entities, with the intention of stealing information or money. This strategic manipulation is known as social engineering and is a key component of a phishing campaign. Gaining insight into the mechanics of phishing is vital for both individuals and organizations in safeguarding against such cyber threats.
The Evolution of Phishing Attacks
Believe it or not, phishing has a history that dates back to the 1990s, where it all started with hackers impersonating AOL employees and using instant messaging and email to steal passwords and to gain access and control of user accounts. Fast forward to the present day, and phishing attacks have evolved into a sophisticated beast. With the rise of social media, a new form of phishing, known as angler phishing, has emerged. It targets victims through social media platforms, often by impersonating customer support accounts or creating fake profiles.
This shows that as technology advances, so do the tactics of cybercriminals. Therefore, keeping up with the development of phishing attacks is essential in effectively combating them.
Types of Phishing Techniques
Now that we’ve gotten a sense of what phishing is and its evolution, let’s take a closer look at the different types of phishing techniques. Just like a skilled angler uses different types of bait to catch a variety of fish, cybercriminals use a myriad of common phishing tactics and techniques to ensnare their victims. These techniques include:
- Email phishing
- Spear phishing
- Whaling
- Vishing (voice phishing)
- Smishing (SMS phishing)
Each of these techniques has unique characteristics and targets, from the general masses to high-ranking individuals within an organization.
Let’s delve deeper into each one.
Email Phishing
Email phishing, a common tactic employed by cybercriminals, involves the perpetrator posing as a reliable individual or entity and revealing personal information in an email. The email is crafted in such a convincing manner that it deceives the recipient into sharing sensitive information or clicking on harmful links, ultimately leading to a successful phishing attack and demonstrating how phishing works.
Imagine receiving an email from your bank asking you to update your account information by clicking on a link. You might think nothing of it and click the link, not realizing that it’s a phishing email and the link leads to a malicious website.
Spear Phishing
While email phishing casts a wide net to catch as many victims as possible, spear phishing takes a more targeted approach. It focuses on specific individuals or a small group, using personalized tactics to infiltrate organizations and compromise their security.
For example, a https phishing perpetrator might email an employee, pretending to be the company’s CEO and asking the employee to wire funds to a certain account. Given the personalized nature of the attack, the employee might not think twice before carrying out the request, making spear phishing a particularly dangerous threat.
Whaling
If spear phishing targets individuals, whaling targets the big fish – high-ranking individuals within an organization such as executives. The cybercriminals use carefully crafted phishing messages to deceive these individuals into providing sensitive information or authorizing fraudulent transactions. The high stakes involved in whaling attacks make them particularly devastating.
For instance, a successful whaling attack on a CEO could lead to significant financial losses and even shake investor confidence.
Vishing
Vishing, or voice phishing, is executed through caller ID spoofing and internet phone calls combined with social engineering strategies. Imagine receiving a call from your bank asking for your account details to verify your identity. It sounds legitimate, right? But it could be a vishing attack, or clone phishing, and by providing the requested information, you could be handing your financial details over to a cybercriminal.
Therefore, exercising caution with unexpected calls and avoiding sharing personal details over the phone is key to preventing such scams.
Smishing
Last but not least, there’s smishing, which involves the use of mobile phones for phishing through text messages or SMS. For instance, you might receive a text message claiming that you’ve won a prize and need to click on a link to claim it. But when you click the link, you’re taken to a malicious website that steals your personal information or installs malware on your device.
Given the ubiquity of mobile phones, smishing poses a substantial risk, highlighting the importance of recognizing its indicators and guarding oneself against it.
Recognizing and Identifying Phishing Emails

Given the myriad of phishing techniques in existence, understanding how to detect and identify phishing emails becomes critical. Typical signs of phishing emails encompass:
- An urgent tone
- Grammar errors
- A sense of urgency in the message and subject line
- Uncommon words or phrases in the subject line
- Alerts from email service providers
- Threats of severe repercussions
- Spelling mistakes
- Unusual requests
- Peculiar content
- Requests for personal information
Being able to spot these signs and report phishing emails can help you avoid falling prey to phishing scams.
Anatomy of a Fake Website

Fake websites constitute a significant element in phishing attacks. They are designed to mimic legitimate websites, tricking users into entering their login credentials or other sensitive information. These websites often use a domain name that closely resembles the legitimate sender’s address but one with subtle misspellings or alterations to fool users.
To verify a website’s legitimacy, one can examine the security certificate by double-clicking on it to view its properties and details or by clicking on the padlock icon in the browser’s address bar to check if the connection to the site is secure.
Common Themes in Phishing Scams

Just as a con artist might use common strategies to swindle their victims, phishing scams often use common themes to trick their targets. Some common themes used in phishing scams include:
- Urgent requests to compel victims to act quickly
- Financial incentives such as prizes or lottery winnings to entice victims into revealing their personal information
- Impersonating trusted entities, such as banks or government agencies, to gain the trust of their victims.
Being aware of these common themes can help you stay one step ahead of phishing scams.
Consequences of Falling for Phishing
The consequences of falling for a phishing attack can be devastating. Not only can it result in significant financial losses, but it can also lead to identity theft and data breaches. The repercussions are not just financial, but also emotional, as falling for a phishing scam can shake one’s confidence and lead to a sense of violation and stress.
Hence, understanding the potential consequences of phishing is crucial in emphasizing the importance of vigilance and prevention.
Protecting Yourself from Phishing: Tips and Tools
So, how can you protect yourself from phishing? The key lies in:
- Being cautious with links and attachments
- Using security software
- Staying informed about common scams
- Employing a password manager to generate and store lengthy, random passwords for each account
- Refraining from sharing passwords with others
- Utilizing unique passwords for various accounts
- Utilizing multi-factor authentication when possible
These measures can greatly enhance your defenses against phishing attacks.
Remember, prevention is always better than cure.
Social Media Phishing: Risks and Precautions
In the age of social media, phishing has taken on a new dimension. Social media phishing targets popular platforms like:
With the intention of acquiring sensitive data for illicit purposes, these attacks often involve the creation of fake profiles, impersonation of friends or family, or direct messages with malicious links and malicious attachments.
Hence, to stay safe on social media, it is advisable to:
- Practice caution when using social media
- Decline friend requests from strangers
- Authenticate any suspicious messages before clicking on links or divulging personal information.
Creating Strong Passwords and Using Password Management Tools
Having a strong, unique password is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to protect against phishing. A robust password is a minimum of 12 characters in length, comprising a mix of:
- uppercase letters
- lowercase letters
- numbers
- symbols
In addition to creating strong passwords, using a password management tool can help to securely manage all your passwords in a centralized location.
Hence, dedicating time and effort to the creation and management of robust passwords is of utmost importance.
Reporting Phishing Attempts: How and Where
If you come across a phishing attempt, it is important to report it to the appropriate authorities or respective companies. Reporting phishing attempts not only helps to combat cybercrime but also plays a crucial role in safeguarding others from becoming victims. Whether you’re reporting to email service providers like Google and Microsoft, tech giants like Apple, or social media platforms like Facebook, your efforts can contribute significantly to the fight against phishing.
The Role of Awareness and Training in Preventing Phishing
Awareness and training play a crucial role in the prevention of phishing. By enabling individuals and teams to:
- Recognize phishing attacks
- Safeguard data
- Access training resources
- Educate employees about potential risks
Organizations can significantly up email security to reduce their vulnerability to phishing attacks.
Hence, it is imperative for organizations to commit resources towards comprehensive phishing awareness and training initiatives.
Real-Life Examples of Phishing Scams
To fully understand the insidious nature of phishing, let’s look at some real-life examples. From the phishing attack that targeted tech giants Facebook and Google, to the phishing scam that tricked individuals into believing they had won a Netflix subscription, these real-life examples illustrate the cunning tactics used by cybercriminals and the devastating consequences for the victims. They serve as a stark reminder of the importance of vigilance and education in the fight against phishing.
Human Error: The Weak Link in Phishing Defense
Despite all the technological defenses we can put in place, human error often remains the weak link in phishing defense. This is because phishing attacks often rely on manipulating human emotions and exploiting trust. From clicking on suspicious links or attachments without proper scrutiny to not exercising caution with passwords, these common errors can lead to successful phishing attacks.
Hence, fostering education and awareness is key to minimizing human error and fortifying our defenses against phishing.
Mobile Phishing: Unique Risks and Warning Signs
Mobile phishing has emerged as a significant threat with the rise of smartphones and tablets. Mobile phishing specifically targets mobile devices and employs a range of tactics to deceive users into disclosing sensitive information. Given the unique risks and warning signs associated with mobile phishing, users must be particularly cautious when using mobile devices for online activities.
The Future of Phishing: Emerging Trends and Threats
Looking ahead, it’s evident that phishing will persistently adapt, posing novel threats. From a 61% increase in attack rates in the latter half of 2022 compared to the previous year to a substantial 356% growth in advanced phishing attacks, these trends underscore the imperative for sustained vigilance.
Moreover, with cybercriminals continuously adapting their tactics with technological advancements, we need to stay one step ahead by staying informed and adapting our defenses accordingly.
Educating the Younger Generation about Phishing
As phishing attacks become more sophisticated, educating the younger generation about this threat is becoming increasingly important. Children and teenagers are often targeted in phishing attacks due to their perceived vulnerability and potential lack of experience in recognizing and defending against cyber scams. Hence, it becomes indispensable to initiate education about how phishing attacks work even for children at a young age, aligning with their initial interactions with smart devices and technology.
By doing so, we can equip them with the knowledge and skills they need to protect themselves from cyber threats.
Global Phishing Laws and Regulations
Legal measures against phishing vary by country, with 156 countries having enacted cybercrime legislation. In the United States, phishing can be subject to prosecution under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) or as wire fraud, among other potential infractions.
These global efforts underscore the seriousness of the phishing threat and the commitment of governments and international organizations to combating it.
Summary
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the world of phishing – from its definition and various techniques to its devastating consequences and robust defenses. We have also discussed the importance of education and awareness in preventing phishing, the role of human error, and the future trends in phishing. As we navigate this digital age, let’s remember to stay vigilant, stay informed, and stay safe!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is phishing 101?
Phishing is a cyberattack where the attacker tricks the target into disclosing sensitive personal information about, revealing login credentials, or transferring money. It occurs predominantly via email and is not personalized for an individual target.
What are the 4 types of phishing?
The four main types of phishing are spear phishing, vishing, smishing, and whaling. It’s important to be aware of these tactics to protect yourself from cyber threats.
What is phishing and why is it a threat?
Phishing is a serious threat as it can result in financial loss, identity theft, and data breaches by deceiving individuals into providing sensitive information through emails or through malicious apps or websites.
How can I identify a phishing email?
Look for signs of urgency, grammatical errors, and implausible threats or requests to identify a phishing email. Don’t fall for these red flags.
What can I do to protect myself from phishing?
To protect yourself from phishing, be cautious with links and attachments, use security software, and stay informed about common scams. Stay vigilant to avoid falling victim to phishing attacks.