Public-private partnerships can be a powerful strategy for building strong cyber security. It is a collaboration between the government and private sector to protect citizens and businesses from cyber threats. Private-public partnerships have long been a part of national cyber security strategies, but what exactly is it?
According to a breach report by IBM 2022, damages from cybercrime have reached 4.35 million in 2022.
Public and private partnerships are critical for critical infrastructure protection from cyber threats. Businesses and government agencies can more effectively identify and address critical vulnerabilities by working together in cyber security. By sharing information and resources, these partnerships can also help improve the cyber ecosystem’s overall security. In addition, these partnerships can help to ensure that critical infrastructure is better protected in the event of a cyber attack.
In response to the cyber security threat, the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA) launched the Joint Cyber Defense Collaborative, which aims to increase public-private cooperation and information sharing. The Collaborative is a forum for government and industry to discuss cyber security threats and collaborate on solutions. Through Collaborative, CISA works to identify best practices for information sharing and incident response.
What is a Public-Private Partnership in cyber security?
A public-private partnership is a collaborative arrangement between two or more public or private entities. These partnerships are often established to complete a specific project, such as building a bridge or to provide funding for an organization, such as the arts.
PPPs may be established to increase innovation and efficiency in the public sector. The government entities provide funding for research and development that would not otherwise be possible in the private sector. In contrast, private companies may contribute their expertise in a particular area.
Of course, a collaboration between industry and government is a vital component in implementing successful cyber security initiatives. Recently, the Department of Health and Services and the National Institutes of Science developed standardized data-sharing guidelines for various industry sectors across the state. There’ll be a big difference here. Sharing data helps the government and industry keep updated about upcoming virus threats and malware. Information sharing establishes working protocols to support forensics and resilience critical to business operations and ensure security against cybercrime.
These partnerships are essential because they provide an open communication line between the government and businesses. This allows for the timely sharing of information that can be used to protect our nation’s critical infrastructure.
PPPs between the government and private companies can help to fill critical gaps in our defenses and make our country more secure. For example, PPPs can help to:
Develop new and innovative security solutions:
The private sector has the expertise and resources to develop innovative security solutions that can be used to defend against cybercrime and other online threats.
Implement effective security measures:
The public sector is responsible for ensuring that security solutions are implemented effectively. PPPs can help to ensure that security solutions are implemented in a way that is aligned with our national security objectives.
Share information and resources:
PPPs can help to ensure that information and resources are shared between the private and public sectors in a way that helps to improve our overall security.
The United States government is committed to working with the private sector to strengthen cyber defenses. PPPs are essential to our national security strategy and can play a crucial role in protecting our country against cybercrime and other online threats.
Three types of PPPs in cybersecurity
There are three primary types of PPPs in cybersecurity: information sharing, cooperative research and development, and operational partnerships. Each type of partnership has its benefits and challenges, but all can help organizations improve their cybersecurity if used correctly.
The first type of PPP is an information-sharing partnership.
These partnerships help organizations share information about cybersecurity threats, vulnerabilities, and incidents. Information sharing can help organizations improve their situational awareness and make better decisions about how to protect their systems and data.
One example of an information-sharing partnership is the Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA), founded in 2014 by a group of leading cybersecurity companies. The CTA is a nonprofit organization that shares information about cybersecurity threats among its member companies. The CTA also produces reports and analyses of trends in cybercrime.
The second type of PPP is a cooperative research and development partnership.
These partnerships are designed to help organizations develop new cybersecurity technologies and solutions jointly. Collaborative research and development can help organizations accelerate the pace of innovation and bring new capabilities to market faster.
One example of a cooperative research and development partnership is the Cyber Security R&D Center, which was founded in 2013 by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
The third type of PPP is an operational partnership.
These partnerships help organizations share resources, personnel, and expertise to improve their cybersecurity posture. Operational partnerships can help organizations better use existing capabilities and improve their responsiveness to cybersecurity threats.
One example of an operational partnership is the National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center (NCCIC), which DHS established in 2009. The NCCIC is a 24/seven cyber situational awareness, incident response, and coordination center that integrates intelligence from multiple sources to provide actionable information to the government and private sector partners.
The United States government is committed to working with the private sector to strengthen cyber defenses. PPPs are essential to our national security strategy and can play a crucial role in protecting our country against cybercrime and other online threats.
Information sharing is the most common type of public-private partnership (PPP) in cybersecurity. These partnerships allow organizations to share information about cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and incidents. The benefits of these partnerships include increased situational awareness and the ability to respond to incidents quickly. However, information-sharing alliances can also be challenging, requiring organizations to trust each other with sensitive information.
Challenges to overcome to create successful partnerships
Maintaining trust is one of the most difficult challenges for both the government and private sectors when it comes to sharing information. For information-sharing partnerships to be successful, both parties need to trust that the information they share will be used responsibly and with respect for privacy and confidentiality. So, it’s crucial to define roles and goals.
The trouble is that governments are averse to disclosing information. However, Canada has adopted legislation allowing for private-sector and government-agency cooperation in the area of intelligence sharing, but it isn’t being put to good use. The law has been successful in the United States, however.
It can also be difficult for organizations to find the resources and personnel needed to participate in operational partnerships. These partnerships require a significant commitment of time and resources, and they can be challenging to sustain over the long term.
Examples of successful public-private partnerships
Several successful PPPs have been created to improve cyber security. One example is the National Cybersecurity and Communications Integration Center (NCCIC), a partnership between the Department of Homeland Security and the private sector. The NCCIC provides information about cyber threats to the government and the private sector and helps coordinate responses to cyber incidents.
Another example of a successful public-private partnership is the Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA), a consortium of private companies that share information about cyber threats. The CTA was founded in 2014 and now has more than 30 members, including major companies such as Microsoft, IBM, and Symantec.
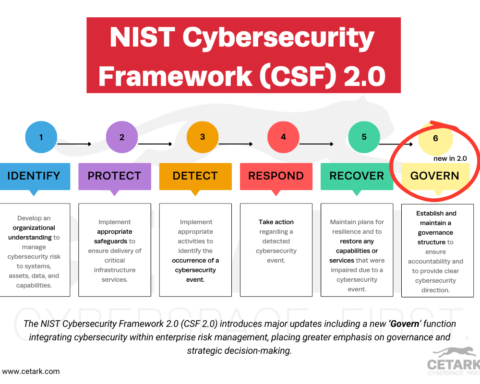
The public and private sectors have also partnered to create several initiatives designed to improve cybersecurity. One example is the Cyber Security Framework, developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2014. The Cybersecurity Framework guides businesses in improving their cyber security posture, and companies worldwide are now using it.
In addition, the public and private sectors have partnered to create several information-sharing platforms. These platforms allow businesses and government agencies to share information about the cyber threat in real-time, which can help to improve our overall cyber security posture.
Conclusion
PPPs are essential for improving our cybersecurity posture and a necessary part of national cyber security strategies. The public sector can provide the government with information about emerging threats, and the government can use this information to develop better cybersecurity policies. In addition, the public and private sectors can invest in research and development to create new technologies that can help protect our critical infrastructure. Despite the challenges, there are several ways that the public and private sectors can work together to strengthen our cyber defenses.